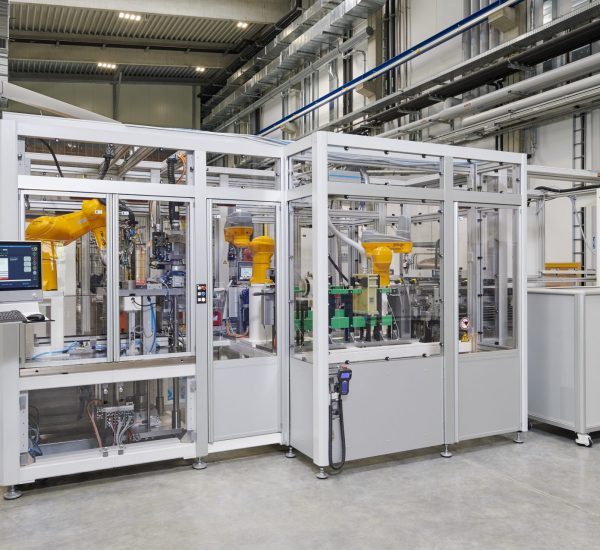
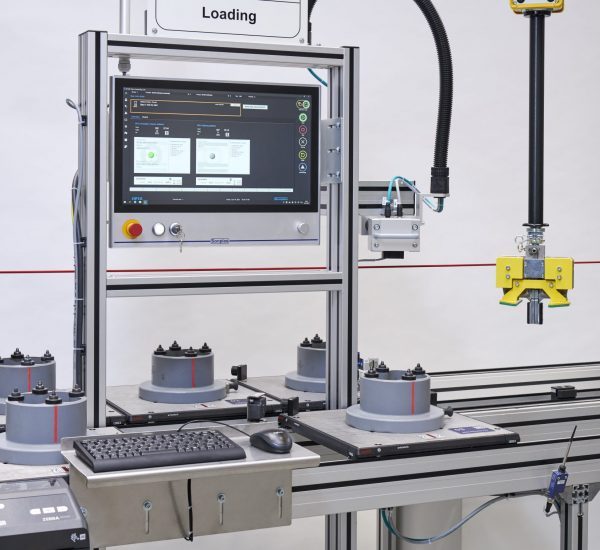
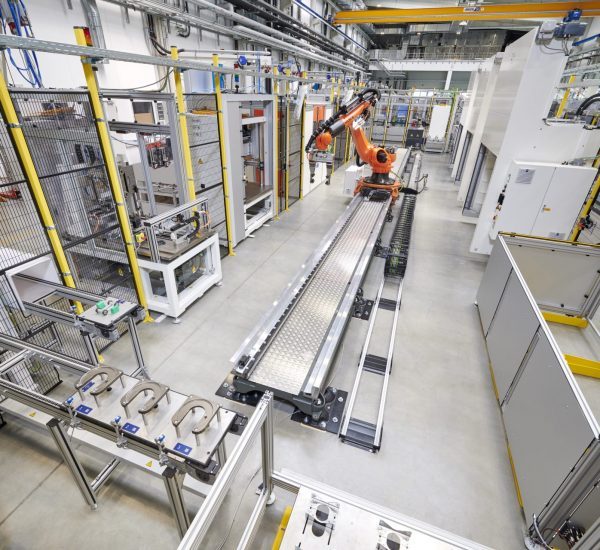
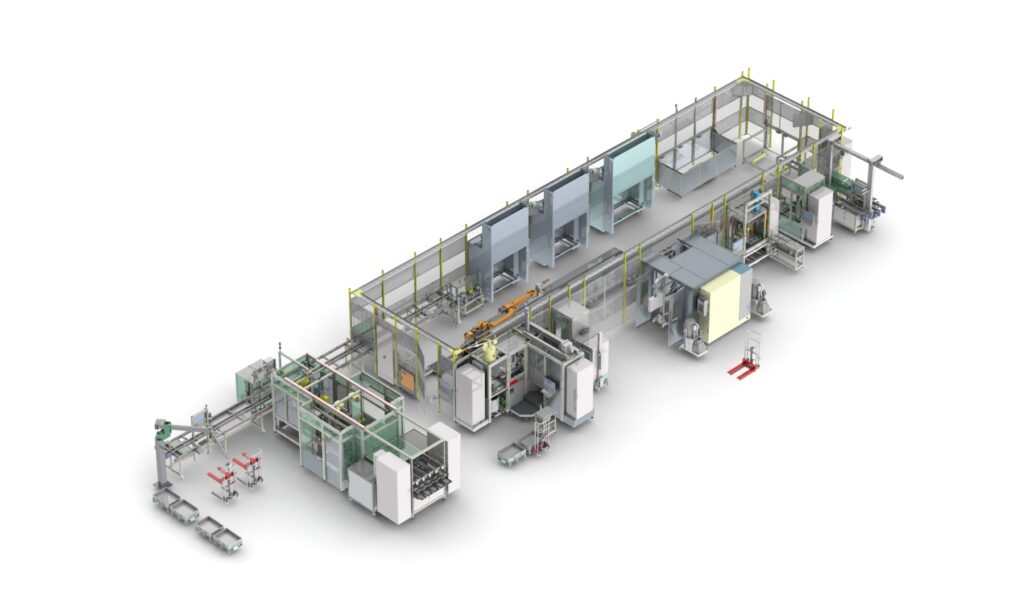
Sonplas developed a partially automated system for cost-efficient and flexible assembly. This comprises multiple stations. In the process, the data connection to the customer’s system can be adapted individually.
At the beginning, there is a well-organised manual workplace for position-oriented loading of the components. A conveyor belt forwards these on work-piece carriers. This is followed by automated loading of magnets by means of a special bonding and assembly procedure. The conveyor belt moves the components to a robotic cell, which integrates other automatic processing stations. The modules are accessible from outside, but at the same time, they are integrated in the protective space in the cell, in which a 7-axis robot takes over component handling. Down the line, an integrated cold shrinking process permits cooling down of the shaft via liquid nitrogen in order to be able to fit it thereafter into the rotor package. After laser marking, adhesive curing, balancing and final assembly, the final electrical and mechanical inspection of the rotors takes place. In addition, a further visual inspection is done by the operator. Thanks to the modular design, the assembly plant can be adapted both in terms of hardware and software to similar rotors.
Highlights
- Standard software concept across the entire line
- Stand-alone stations (that can be integrated as independent machines in other production lines)
- Parts handling by means of a 7-axis robot
- Independent nitrogen cooling system for cooling the shaft
- Flexible, mobile pressing system complying with predefined clamping forces
Processes
- Pallet transport handling / Loading via work-piece carrier system
- Component identification (position/type)
- Cooling (liquid nitrogen) / Cold shrink fitting
- Fitting / Pressing in and magnetising
- Adhesive application (travelling down different adhesive tracks via 6-axis robot)
- Rotor handling with 7-axis robot
- Laser marking
- Curing the adhesive (Heating up and cooling down)
- Determining and eliminating the imbalance
- Geometric, electrical, magnetic testing and visual optical inspection
- Rework
- Unloading and packaging